Unveiling Redox-Driven Mineral And Organic Interactions On Mars' Jezero Crater
Welcome to your ultimate source for breaking news, trending updates, and in-depth stories from around the world. Whether it's politics, technology, entertainment, sports, or lifestyle, we bring you real-time updates that keep you informed and ahead of the curve.
Our team works tirelessly to ensure you never miss a moment. From the latest developments in global events to the most talked-about topics on social media, our news platform is designed to deliver accurate and timely information, all in one place.
Stay in the know and join thousands of readers who trust us for reliable, up-to-date content. Explore our expertly curated articles and dive deeper into the stories that matter to you. Visit Best Website now and be part of the conversation. Don't miss out on the headlines that shape our world!
Table of Contents
Unveiling Redox-Driven Mineral and Organic Interactions on Mars' Jezero Crater: A New Chapter in the Search for Life
The quest to understand Mars' past habitability and potential for past or present life has taken a significant leap forward. New research, published in [Insert Journal Name and Link Here], unveils compelling evidence of complex redox-driven interactions between minerals and organic molecules within Jezero Crater, a key target for astrobiological exploration. This groundbreaking discovery significantly enhances our understanding of the Martian environment and its potential to support life.
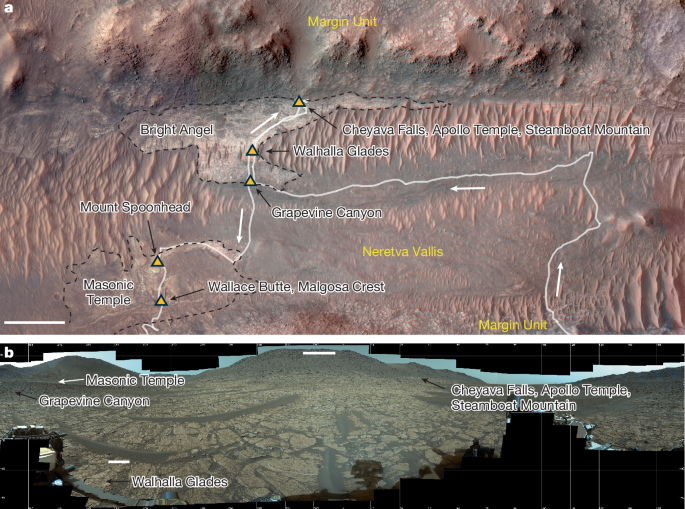
Jezero Crater: A Prime Location for Astrobiological Investigation
Jezero Crater, a 49-kilometer-wide impact crater located on the western edge of Isidis Planitia, has long captivated scientists due to its compelling geological history. Evidence suggests that Jezero was once home to a lake, fed by a river delta system, billions of years ago. This ancient lake environment provides a unique opportunity to search for biosignatures – evidence of past or present life – preserved within the crater's sedimentary rocks. The presence of clays and carbonates, minerals often formed in the presence of water, further strengthens Jezero’s importance in the search for extraterrestrial life.
Redox Reactions: A Key to Understanding Martian Chemistry
The new research focuses on redox reactions, which involve the transfer of electrons between molecules. These reactions are fundamental to many biological processes on Earth and are crucial for understanding the chemical evolution of planetary bodies. The study reveals evidence of significant redox-driven interactions between various minerals – including iron oxides, sulfates, and clays – and organic molecules within Jezero Crater’s geological formations.
The Significance of Organic Molecule Detection
The detection of organic molecules, the building blocks of life as we know it, is not new on Mars. However, the context within which these molecules are found is critical. This study highlights the importance of analyzing the interaction between these organic molecules and the surrounding minerals. The redox processes identified suggest a dynamic chemical environment capable of influencing the preservation and alteration of organic matter. This understanding is crucial for interpreting the significance of any detected organic molecules.
Implications for Past Habitability
The findings strongly suggest a more complex and potentially habitable environment within Jezero Crater than previously thought. The diverse range of mineral-organic interactions detected indicates a dynamic interplay of chemical processes that could have supported microbial life. The preservation of organic molecules, influenced by redox reactions, offers valuable insights into the potential for long-term preservation of biosignatures.
Future Exploration and Research
This research emphasizes the importance of continued exploration of Jezero Crater and other promising locations on Mars. Future missions, including sample return missions, will play a vital role in further investigating these redox-driven interactions and determining the ultimate significance of these findings for the search for life beyond Earth.
Key Takeaways:
- Complex Redox Interactions: The study reveals complex redox interactions between minerals and organic molecules in Jezero Crater.
- Enhanced Habitability Potential: This indicates a more complex and potentially habitable environment than previously understood.
- Importance of Mineral-Organic Interactions: The study stresses the importance of understanding the interaction between minerals and organic molecules for interpreting biosignatures.
- Future Exploration Needs: Continued exploration and sample return missions are crucial for further investigation.
This discovery represents a significant advancement in our understanding of Mars and its potential for past or present life. It underscores the importance of continued research and exploration to unravel the secrets of the Red Planet. Further analysis of data from the Perseverance rover and future missions holds the key to unlocking even more profound insights into the fascinating history of Jezero Crater.

Thank you for visiting our website, your trusted source for the latest updates and in-depth coverage on Unveiling Redox-Driven Mineral And Organic Interactions On Mars' Jezero Crater. We're committed to keeping you informed with timely and accurate information to meet your curiosity and needs.
If you have any questions, suggestions, or feedback, we'd love to hear from you. Your insights are valuable to us and help us improve to serve you better. Feel free to reach out through our contact page.
Don't forget to bookmark our website and check back regularly for the latest headlines and trending topics. See you next time, and thank you for being part of our growing community!
Featured Posts
-
 Secure Your 300 Fan Duels Nfl Sunday Promo Code Inside
Sep 15, 2025
Secure Your 300 Fan Duels Nfl Sunday Promo Code Inside
Sep 15, 2025 -
 Big Ten Football History Rewritten Ferentzs Record Breaking Win
Sep 15, 2025
Big Ten Football History Rewritten Ferentzs Record Breaking Win
Sep 15, 2025 -
 Starlink Down Widespread Internet Disruption Affects Ukraine And Global Users
Sep 15, 2025
Starlink Down Widespread Internet Disruption Affects Ukraine And Global Users
Sep 15, 2025 -
 Devastating Finish Villanova Td Spoils Penn State Cover In 2025 Cfb Game
Sep 15, 2025
Devastating Finish Villanova Td Spoils Penn State Cover In 2025 Cfb Game
Sep 15, 2025 -
 Is Brent Prys Seat Getting Hot Virginia Techs Struggles Continue
Sep 15, 2025
Is Brent Prys Seat Getting Hot Virginia Techs Struggles Continue
Sep 15, 2025
 Nfls Top Backup Quarterbacks Who Could Spearhead A Playoff Run In 2024
Nfls Top Backup Quarterbacks Who Could Spearhead A Playoff Run In 2024
