Redox-Driven Mineral And Organic Interactions: A Study Of Jezero Crater Sedimentary Rocks
Welcome to your ultimate source for breaking news, trending updates, and in-depth stories from around the world. Whether it's politics, technology, entertainment, sports, or lifestyle, we bring you real-time updates that keep you informed and ahead of the curve.
Our team works tirelessly to ensure you never miss a moment. From the latest developments in global events to the most talked-about topics on social media, our news platform is designed to deliver accurate and timely information, all in one place.
Stay in the know and join thousands of readers who trust us for reliable, up-to-date content. Explore our expertly curated articles and dive deeper into the stories that matter to you. Visit Best Website now and be part of the conversation. Don't miss out on the headlines that shape our world!
Table of Contents
Redox-Driven Mineral and Organic Interactions: Unraveling the Mysteries of Jezero Crater
The search for ancient life on Mars has taken a significant leap forward with the analysis of sedimentary rocks from Jezero Crater, a once-water-rich environment now under intense scrutiny by NASA's Perseverance rover. A groundbreaking new study published in [Insert Journal Name Here] sheds light on the complex interplay between redox reactions and the preservation of both mineral and organic molecules within these rocks, offering tantalizing clues about the planet's past habitability.
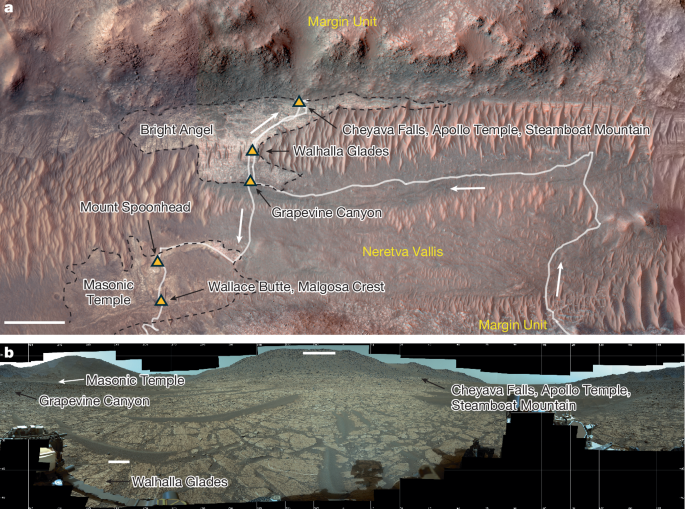
Jezero Crater: A Martian Oasis in the Past?
Jezero Crater, chosen for its potential to reveal evidence of past microbial life, is believed to have once housed a lake and a river delta. This ancient aqueous environment provided ideal conditions for the formation and preservation of organic molecules – the building blocks of life as we know it. The Perseverance rover's mission has been pivotal in collecting samples from various locations within the crater, allowing scientists to delve into the geological history and potential biosignatures of this intriguing Martian landscape.
The Role of Redox Reactions in Preserving Biosignatures
The study focuses on the crucial role of redox reactions – chemical processes involving electron transfer – in shaping the Jezero Crater sedimentary rocks. These reactions are fundamental in controlling the preservation and degradation of organic molecules. The researchers found evidence of:
- Oxidative Processes: These processes can break down organic molecules, rendering them undetectable. Understanding the extent of oxidation is crucial for assessing the survival of any potential biosignatures.
- Reductive Processes: Conversely, reductive environments can help protect and even synthesize organic molecules, creating favorable conditions for their preservation. The identification of these environments is a key objective in the search for past life.
- Mineral Interactions: The study highlights the close relationship between mineral composition and the redox state of the environment. Specific minerals act as catalysts or reactants in redox reactions, influencing the fate of organic molecules. For example, the presence of certain clays might have played a crucial role in preserving organic matter.
Implications for the Search for Martian Life
This research underscores the importance of considering the complex interplay between minerals and organic molecules within the context of redox processes. Understanding these interactions is essential for interpreting the data collected by the Perseverance rover and future Mars exploration missions. The findings suggest that:
- Targeted Sampling: Future sample collection should prioritize areas with specific mineral compositions and redox conditions known to be favorable for organic molecule preservation.
- Improved Analytical Techniques: Advanced analytical techniques are needed to detect and characterize subtle signs of past life, especially in areas where oxidative processes have partially degraded organic matter.
- Refinement of Habitability Models: This study contributes to refining models of Martian habitability, improving our understanding of the conditions that may have supported life in the past.
Looking Ahead: The Next Steps in Martian Exploration
The Perseverance rover's mission is ongoing, and the samples collected will eventually be returned to Earth for more detailed analysis. This future research, combined with ongoing studies like the one described here, promises to significantly advance our understanding of Jezero Crater and the potential for past life on Mars. The quest to unravel the mysteries of the red planet continues, fueled by discoveries like this which highlight the intricate relationship between geology, chemistry, and the potential for life beyond Earth. Stay tuned for further updates as this exciting research unfolds. [Link to NASA's Mars Exploration Program]
Keywords: Jezero Crater, Mars, Perseverance rover, redox reactions, organic molecules, biosignatures, Martian life, sedimentary rocks, mineral interactions, habitability, Mars exploration, NASA.

Thank you for visiting our website, your trusted source for the latest updates and in-depth coverage on Redox-Driven Mineral And Organic Interactions: A Study Of Jezero Crater Sedimentary Rocks. We're committed to keeping you informed with timely and accurate information to meet your curiosity and needs.
If you have any questions, suggestions, or feedback, we'd love to hear from you. Your insights are valuable to us and help us improve to serve you better. Feel free to reach out through our contact page.
Don't forget to bookmark our website and check back regularly for the latest headlines and trending topics. See you next time, and thank you for being part of our growing community!
Featured Posts
-
 Chainsaw Man Film Reze Arc Us Release Date Announced October 24th
Sep 15, 2025
Chainsaw Man Film Reze Arc Us Release Date Announced October 24th
Sep 15, 2025 -
 Chisholm Jr On Yankees Surge We Re The Team To Beat Marlins Confidence High
Sep 15, 2025
Chisholm Jr On Yankees Surge We Re The Team To Beat Marlins Confidence High
Sep 15, 2025 -
 Elon Musks Starlink Experiencing Widespread Service Disruption
Sep 15, 2025
Elon Musks Starlink Experiencing Widespread Service Disruption
Sep 15, 2025 -
 Major Starlink Outage Affecting Thousands Causes And Potential Solutions
Sep 15, 2025
Major Starlink Outage Affecting Thousands Causes And Potential Solutions
Sep 15, 2025 -
 Chainsaw Man The Movie Reze Arc Us Release Date Announced October 24th
Sep 15, 2025
Chainsaw Man The Movie Reze Arc Us Release Date Announced October 24th
Sep 15, 2025
 From Storm To Aces Jewell Loyd On Leaving Seattle And Finding Tranquility In Las Vegas
From Storm To Aces Jewell Loyd On Leaving Seattle And Finding Tranquility In Las Vegas
 Jewell Loyd Finds Peace In Las Vegas After Seattle Storm Drama
Jewell Loyd Finds Peace In Las Vegas After Seattle Storm Drama
 Nfls Top Backup Quarterbacks Who Could Spearhead A Playoff Run In 2024
Nfls Top Backup Quarterbacks Who Could Spearhead A Playoff Run In 2024
